Hypothesis and Conclusion of Mean Value Theorem
Once we have found the p-value or rejection region and made a statistical decision about the null hypothesis ie. Probability Distributions of Continuous Random.

Does The Function Satisfy The Hypotheses Of The Mean Value Theorem Find All Numbers C That Satisfy Youtube
Expected Value Mean and Variance.
. State an overall conclusion. Upon finding the p-value and subsequently coming to a conclusion to reject the Null Hypothesis or fail to reject the Null Hypothesis there is also a possibility that the wrong. In other words after conducting many trials of an experiment you would expect this average value.
In mathematics the mean value theorem states roughly that for a given planar arc between two endpoints there is at least one point at which the tangent to the arc is parallel to the secant through its endpoints. It is one of the most important results in real analysisThis theorem is used to prove statements about a function on an interval starting from local hypotheses about. This long-term average is known as the mean or expected value of the experiment and is denoted by the Greek letter μ.
When evaluating the long-term results of statistical experiments we often want to know the average outcome. The null hypothesis belonging to this F-test is that all of the population coefficients in the model except for the intercept are zero so the. If the random variable is denoted by then it is also known as the expected value of denoted For a discrete probability distribution the mean is given by where the sum is taken over all possible values of the random variable and is the probability.
These two-tailed confidence intervals go hand-in-hand with the two-tailed hypothesis tests we learned in Lesson 5. The mean of a probability distribution is the long-run arithmetic average value of a random variable having that distribution. Notice we do not make a decision where we will accept the null hypothesis.
The conclusion drawn from a two-tailed confidence interval is usually the same as the conclusion drawn from a two-tailed hypothesis test. All of the confidence intervals we constructed in this course were two-tailed. If the p-value is considered significant is less than the specified level of significance the null hypothesis is false and more tests must be done to prove the alternative hypothesis.
We will reject the null or fail to reject the null we then want to summarize our results into an overall conclusion for our. A heteroskedasticity-robust version of this F-test which leads to the same conclusion.

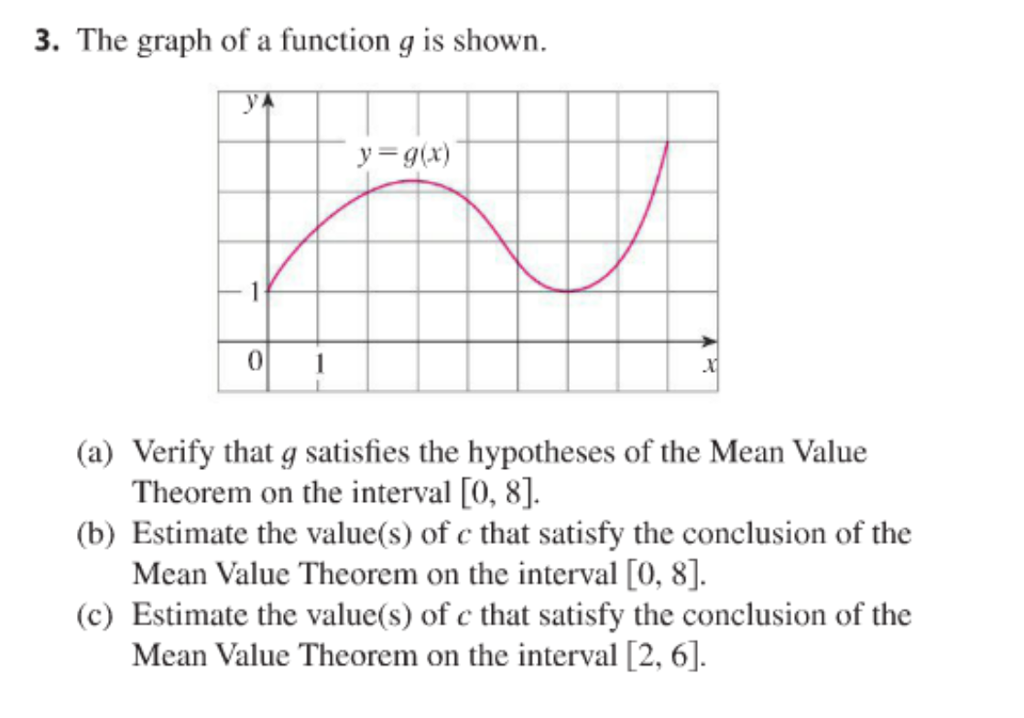
Solved The Graph Of A Function G Is Shown A Verify That Chegg Com
Mean Value Theorem Wyzant Ask An Expert
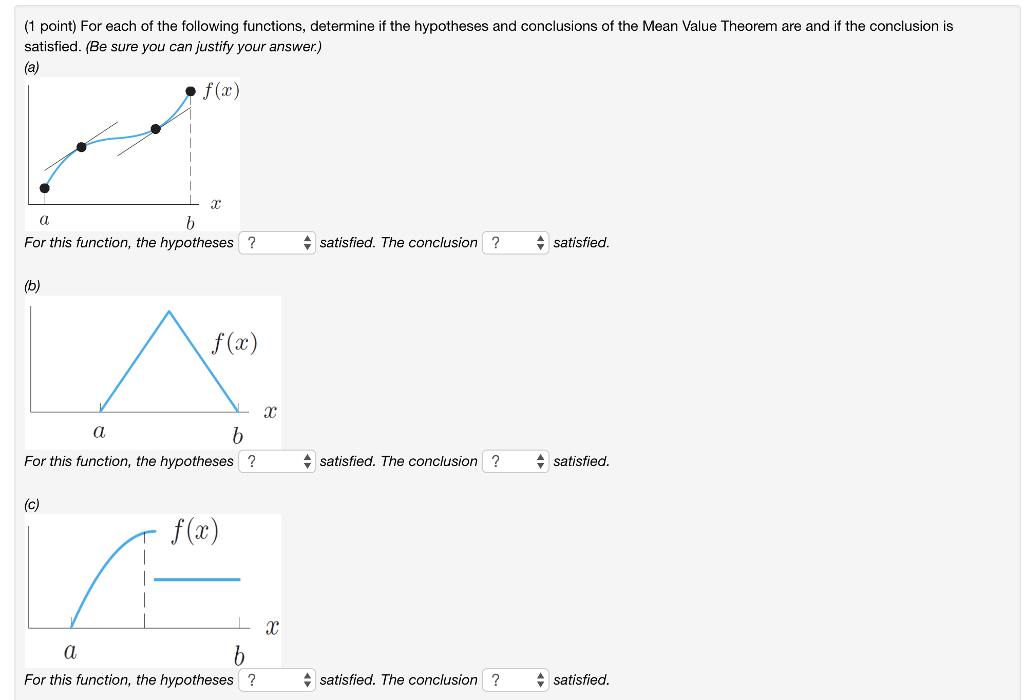
Solved 1 Point For Each Of The Following Functions Chegg Com
No comments for "Hypothesis and Conclusion of Mean Value Theorem"
Post a Comment